MANTIS

- Apache
- PHP
- MySQL
About

MantisBT or Mantis Bug Tracker is an open source popular bug tracking system and the most common use of MantisBT is to track software defects. Yet, MantisBT is often configured by users to serve as a more generic issue tracking system and project management tool. MantisBT lets users track their issues with its simple, intuitive interface. It is an issue tracker, which provides a delicate balance between easiness and power.
Mantis is a pre-configured, ready to run image for running MantisBT on Azure. Mantis Bug Tracker is a web-based bug tracking system written in PHP, MySQL server or mariadb-server, Apache (LAMP).
Developed mainly as a software bug tracker, many organizations implement MantisBT as a generic tool for issue tracking and project management. This platform is simple to set up and ready to go in just a few minutes.
Features of Mantis on Azure
- Plug-ins
- Customizable
- Notifications
- Revision control system integration
- Graphing of relationships between issues
- Project Management & TimeTracking with CodevTT
- Revision control of text fields and notes
Mantis Bug Tracker software allows users to start their work in minutes and manage their projects while collaborating with their teammates and clients effectively. It is simple to split the issues into categories and move them through the issues life-cycle. Search them, auto-assign them to the developers, attach files, tag it, ping your teammates and customize the system.
Why Choose Mantis from Niles Partner?
- MantisBT allows managing the releases with ease.
- MantisBT has its own in-built time tracking feature.
- Get the big picture on the team’s performance!
- Integrate support with the internal issue tracking.
- Improve workflow and efficiency of the development
- Integrate the test management solution with MantisHub.
- Single Sign-on & Auto-Provisioning
- Mantis is supported on iPhone, Android, and Windows Phone Platforms
- MantisBT makes collaboration easy, fast, and professional
MantisBT lets a large number of users to interact and track issues between multiple projects and is usable on any of the main operating systems. It is ideal for companies that either build their own software or need to keep track of software issues. MantisBT can be installed on Linux, Windows, Mac OS, OS/2, and many others.
- Type virtual machines in the search.
- Under Services, select Virtual machines.
- In the Virtual machines page, select Add. The Create a virtual machine page opens.
- In the Basics tab, under Project details, make sure the correct subscription is selected and then choose to Create new resource group. Type myResourceGroup for the name.*.
- Under Instance details, type myVM for the Virtual machine name, choose East US for your Region, and choose Ubuntu 18.04 LTS for your Image. Leave the other defaults.
- Under Administrator account, select SSH public key, type your user name, then paste in your public key. Remove any leading or trailing white space in your public key.
- Under Inbound port rules > Public inbound ports, choose Allow selected ports and then select SSH (22) and HTTP (80) from the drop-down.
- Leave the remaining defaults and then select the Review + create button at the bottom of the page.
- On the Create a virtual machine page, you can see the details about the VM you are about to create. When you are ready, select Create.
It will take a few minutes for your VM to be deployed. When the deployment is finished, move on to the next section.
Connect to virtual machine
Create an SSH connection with the VM.
- Select the Connect button on the overview page for your VM.
- In the Connect to virtual machine page, keep the default options to connect by IP address over port 22. In Login using VM local account a connection command is shown. Select the button to copy the command. The following example shows what the SSH connection command looks like:
bashCopy
ssh azureuser@10.111.12.123
- Using the same bash shell you used to create your SSH key pair (you can reopen the Cloud Shell by selecting >_ again or going to https://shell.azure.com/bash), paste the SSH connection command into the shell to create an SSH session.
Usage/Deployment Instructions
Step 1: Access Mantis from Azure Marketplace and click ON Get it now button.
Click on continue
Now click on create
Step 2: Now to create a virtual machine, enter or select appropriate values for zone, machine type, resource group and so on as per your choice.
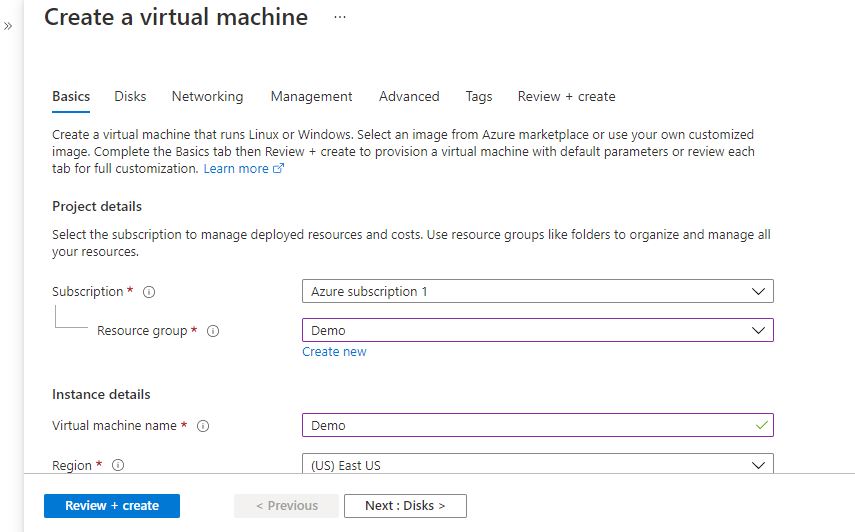
Step 3: Use the browser to access the application at http://<instance ip address> replace <instance ip address> with the actual ip address of the running instance.
Note: You will get the Instance IP Address as shown in the screenshot below:
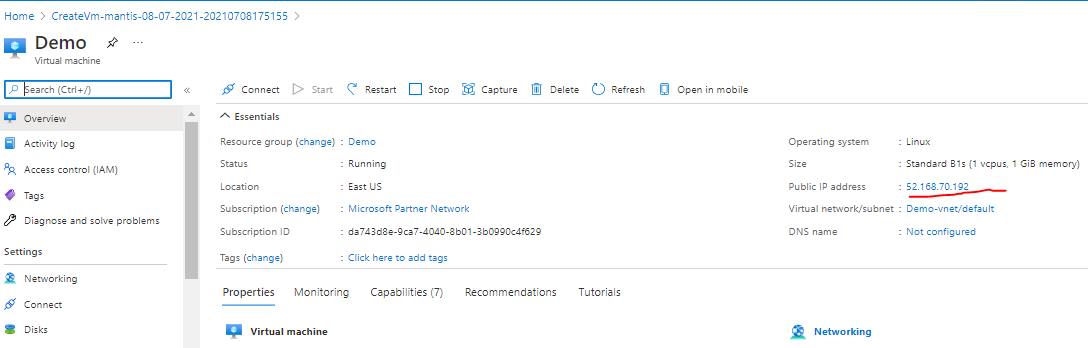
Step 4: Enter the database details :
Username: admin
Password: Niles@123
Database Name: mantis
Admin Username: root
Admin Password: Niles
Scroll to last and click on Create.
Step 5: Login using the default username and password:
Username: administrator
Password: root
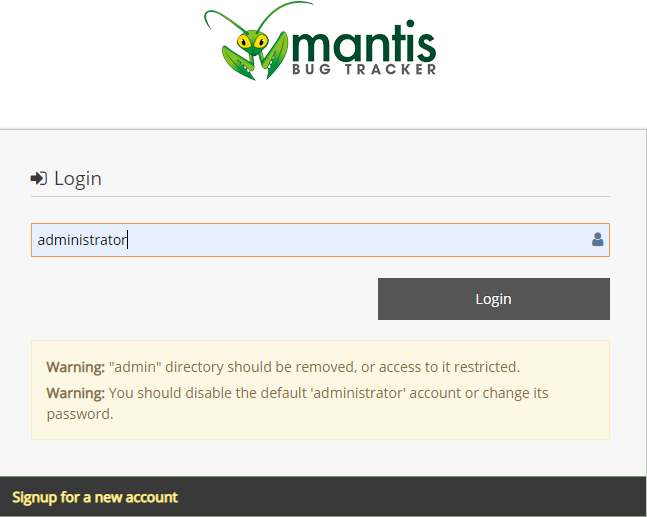
You have to change the default login credentials as soon as your login to the dashboard for the first time.
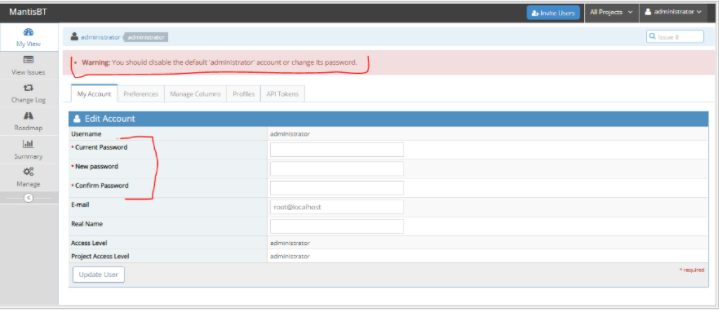
After changing the password, login again to your account and enjoy the application.
- (510) 298-5936
Submit Your Request
Until now, small developers did not have the capital to acquire massive compute resources and ensure they had the capacity they needed to handle unexpected spikes in load. Amazon EC2 enables any developer to leverage Amazon’s own benefits of massive scale with no up-front investment or performance compromises. Developers are now free to innovate knowing that no matter how successful their businesses become, it will be inexpensive and simple to ensure they have the compute capacity they need to meet their business requirements.
The “Elastic” nature of the service allows developers to instantly scale to meet spikes in traffic or demand. When computing requirements unexpectedly change (up or down), Amazon EC2 can instantly respond, meaning that developers have the ability to control how many resources are in use at any given point in time. In contrast, traditional hosting services generally provide a fixed number of resources for a fixed amount of time, meaning that users have a limited ability to easily respond when their usage is rapidly changing, unpredictable, or is known to experience large peaks at various intervals.
Traditional hosting services generally provide a pre-configured resource for a fixed amount of time and at a predetermined cost. Amazon EC2 differs fundamentally in the flexibility, control and significant cost savings it offers developers, allowing them to treat Amazon EC2 as their own personal data center with the benefit of Amazon.com’s robust infrastructure.
When computing requirements unexpectedly change (up or down), Amazon EC2 can instantly respond, meaning that developers have the ability to control how many resources are in use at any given point in time. In contrast, traditional hosting services generally provide a fixed number of resources for a fixed amount of time, meaning that users have a limited ability to easily respond when their usage is rapidly changing, unpredictable, or is known to experience large peaks at various intervals.
Secondly, many hosting services don’t provide full control over the compute resources being provided. Using Amazon EC2, developers can choose not only to initiate or shut down instances at any time, they can completely customize the configuration of their instances to suit their needs – and change it at any time. Most hosting services cater more towards groups of users with similar system requirements, and so offer limited ability to change these.
Finally, with Amazon EC2 developers enjoy the benefit of paying only for their actual resource consumption – and at very low rates. Most hosting services require users to pay a fixed, up-front fee irrespective of their actual computing power used, and so users risk overbuying resources to compensate for the inability to quickly scale up resources within a short time frame.
No. You do not need an Elastic IP address for all your instances. By default, every instance comes with a private IP address and an internet routable public IP address. The private address is associated exclusively with the instance and is only returned to Amazon EC2 when the instance is stopped or terminated. The public address is associated exclusively with the instance until it is stopped, terminated or replaced with an Elastic IP address. These IP addresses should be adequate for many applications where you do not need a long lived internet routable end point. Compute clusters, web crawling, and backend services are all examples of applications that typically do not require Elastic IP addresses.
You have complete control over the visibility of your systems. The Amazon EC2 security systems allow you to place your running instances into arbitrary groups of your choice. Using the web services interface, you can then specify which groups may communicate with which other groups, and also which IP subnets on the Internet may talk to which groups. This allows you to control access to your instances in our highly dynamic environment. Of course, you should also secure your instance as you would any other server.
Highlights
- Free 1-click backup, restore and migrate: bundled backup software saves changes to files, databases and package management to encrypted storage which servers can be automatically restored from.
- Secure, supported and easy to maintain: auto-updated daily with latest security patches. Bundled support for no extra charge.
- Power for administrators